If you are looking for the most practical Google Sheets Formulas Cheat Sheet to speed up your workflow, solve formula errors, and automate data tasks, this guide is for you. Whether you are a small business owner, project manager, financial analyst, educator, or casual user, this resource provides step by step instructions, real world examples, and shortcuts that answer common questions such as:
- What are the most important Google Sheets formulas to learn first?
- How do I fix Google Sheets formula errors quickly?
- How can I combine data from multiple sheets without copy pasting?
- What shortcuts will make working in Sheets faster?
This cheat sheet includes downloadable PDFs, expert tips, and trusted product recommendations like Export emails to Google Sheets to streamline workflows such as importing email data directly into a spreadsheet for analysis.
Table of Contents
- Get the Google Sheets Cheat Sheet
- Essential Google Sheets Functions and How to Use Them
- Real World Use Cases for Sheets Functions
- Top Formula Troubleshooting Tips
- 6 Time Saving Google Sheets Shortcuts
- Advanced Google Sheets Features
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Why Use a Google Sheets Cheat Sheet
- Conclusion
Get the Google Sheets Cheat Sheet
Bookmark this section for quick reference, or download and print this table to keep on hand. Below is a table of the most important Google Sheets formulas, complete with syntax and usage.
| Function | Use | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| SUM | Calculates the sum of a range of cells | SUM(range1, [range2, ...]) |
| AVERAGE | Calculates the average of a range of cells | AVERAGE(range1, [range2, ...]) |
| COUNT | Counts the number of numeric cells in a range | COUNT(range1, [range2, ...]) |
| MAX | Finds the maximum value in a range | MAX(range1, [range2, ...]) |
| MIN | Finds the minimum value in a range | MIN(range1, [range2, ...]) |
| IF | Performs conditional logic based on a condition | IF(logical_expression, value_if_true, value_if_false) |
| VLOOKUP | Searches first column and returns data from a chosen column | VLOOKUP(search_key, range, index, [is_sorted]) |
| CONCAT | Combines two strings into one | CONCAT(string1, string2) |
| CONCATENATE | Combines multiple strings into a single string | CONCATENATE(text1, [text2, ...]) |
| SUBSTITUTE | Replaces specific text within a string | SUBSTITUTE(text, old_text, new_text, [occurrence]) |
| DATE | Creates a date from year, month, day | DATE(year, month, day) |
| TODAY | Returns the current date | TODAY() |
| LEN | Counts all characters in text including spaces | LEN(text) |
| LEFT | Extracts characters from the beginning of text | LEFT(text, num_chars) |
| RIGHT | Extracts characters from the end of text | RIGHT(text, num_chars) |
| MID | Extracts a substring from text | MID(text, start, num_chars) |
| COUNTIF | Counts cells that meet a criterion | COUNTIF(range, criterion) |
| SUMIF | Sums values that meet a criterion | SUMIF(range, criterion, [sum_range]) |
| IFERROR | Returns a value if a formula results in an error | IFERROR(value, [value_if_error]) |
| OFFSET | Returns a reference offset from a starting cell | OFFSET(reference, rows, cols, [height], [width]) |
| ROUND | Rounds a number to set decimals | ROUND(number, num_digits) |
| TRIM | Removes leading and trailing spaces | TRIM(text) |
| FIND | Finds the position of text within text case sensitive | FIND(find_text, within_text, [start_num]) |
| LEFTB | Returns bytes from the start of text | LEFTB(text, num_bytes) |
| RIGHTB | Returns bytes from the end of text | RIGHTB(text, num_bytes) |
| MIDB | Returns bytes from text starting at a byte position | MIDB(text, start_byte, num_bytes) |
| REGEXEXTRACT | Extracts text that matches a regular expression | REGEXEXTRACT(text, regular_expression) |
| REGEXREPLACE | Replaces text that matches a regular expression | REGEXREPLACE(text, regular_expression, replacement) |
| SPLIT | Splits text into columns by delimiter | SPLIT(text, delimiter, [split_by_each]) |
| TRANSPOSE | Switches rows and columns | TRANSPOSE(array) |
| ARRAYFORMULA | Applies a formula to an entire range at once | ARRAYFORMULA(array_formula) |
| IMPORTRANGE | Imports a range from another spreadsheet | IMPORTRANGE(spreadsheet_url, range_string) |
| QUERY | Filters, sorts, and aggregates with SQL like syntax | QUERY(data, query, [headers]) |
| INDEX | Returns the value at a row and column in a range | INDEX(range, row_num, [column_num]) |
5 Essential Google Sheets Functions and How to Use Them
Here are the top formulas every Google Sheets user should master, with clear explanations and real world examples.
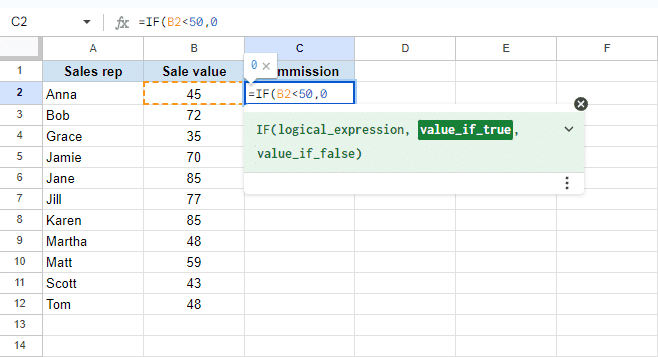
- IF lets you set a condition and decide what happens if it’s true or false. For example, you can check if a sales number is above a target and display “Met Goal” if true, or “Below Goal” if false. This is useful for categorizing, flagging, or triggering other calculations based on your rules.
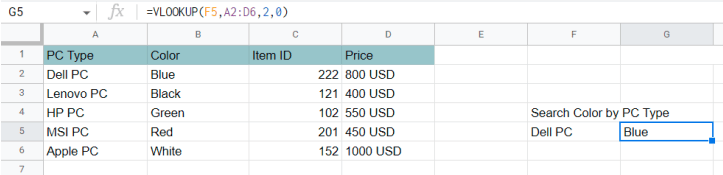
- VLOOKUP searches the first column of your data for a specific value and returns related information from another column in the same row. For example, you could enter a product ID and instantly get its price from a product list without scrolling or manually searching.
- SUMIF adds up only the values that match your chosen criteria. For example, you could total sales from a specific region, or add only orders above $500, helping you focus on the numbers that matter most.

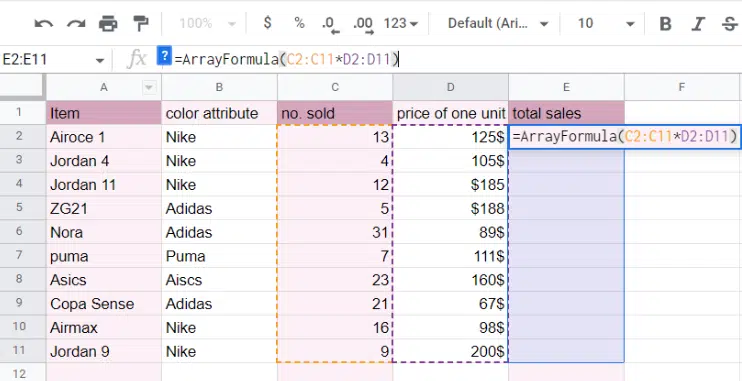
- ARRAYFORMULA automatically applies a formula to an entire range without manually dragging it down. For example, you can calculate a discount for every row in a column at once, saving time when working with large datasets.
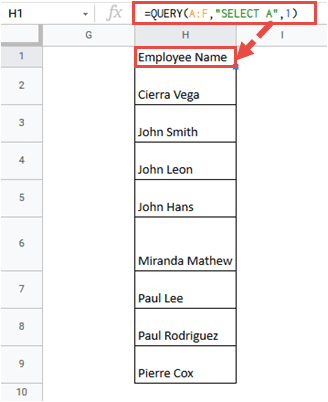
- QUERY uses a simple language to filter, sort, and summarize your data all in one function. For example, you could pull only the orders from January, sort them by total price, and sum the revenue—replacing multiple steps with one command.
Real World Use Cases for Sheets Functions
- Finance teams reconcile invoices with SUMIF and VLOOKUP to flag anomalies quickly.
- Educators merge student grades from multiple sheets using IMPORTRANGE and ARRAYFORMULA.
- Project managers automate task summaries with QUERY and CONCATENATE.
Need to import and analyze email data? Try Export Emails to Google Sheets to automatically pull emails into your spreadsheet for filtering, categorizing, or creating automated reports.
Top Formula Troubleshooting Tips
- Check for extra spaces using TRIM.
- Wrap formulas with IFERROR to show a custom message instead of an error.
- Use COUNTIF to validate expected results quickly.
6 Time Saving Google Sheets Shortcuts
- Autocomplete lets you save time by finishing a function for you. Just start typing a formula name, like
=SUM, and press “Tab” to complete it instantly. If there’s more than one option, Sheets shows a list you can pick from, helping you avoid typos and remember exact function names.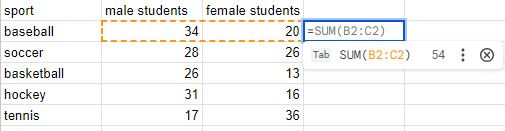
- Keyboard Shortcuts speed up your work without taking your hands off the keyboard. For example, pressing
Ctrl + /on Windows or⌘ + /on Mac opens a complete list of available shortcuts, so you can quickly find the ones that save you the most clicks.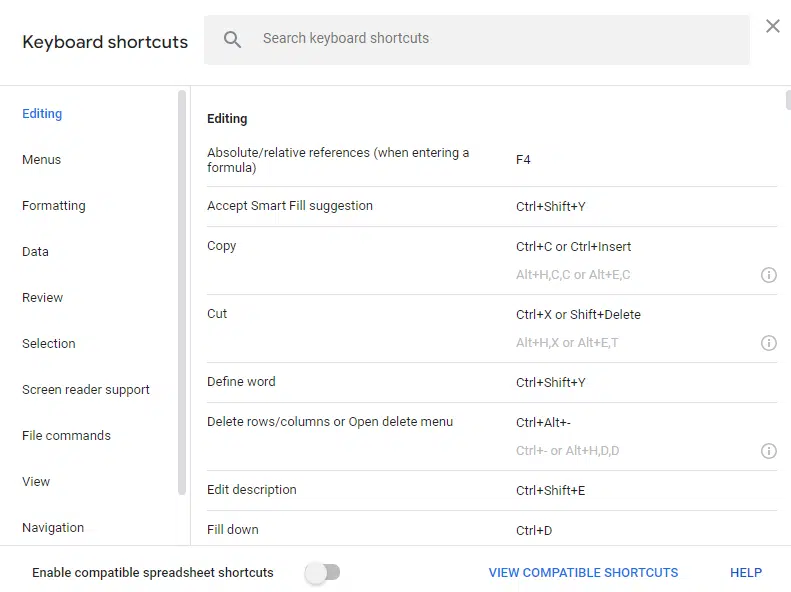
- Select Ranges Rapidly helps you highlight multiple cells faster. Hold Shift while pressing the Arrow keys to extend your selection. For instance, Shift + Down Arrow selects the next cell below, and Ctrl + Shift + Down Arrow selects all contiguous cells in a column until the last filled cell.
- Named Ranges let you give a descriptive name to a cell range, like “Sales_Q1” instead of “A1:A50.” This makes your formulas easier to read, manage, and update, especially in large sheets. You can set these up from the Data menu under “Named ranges.”
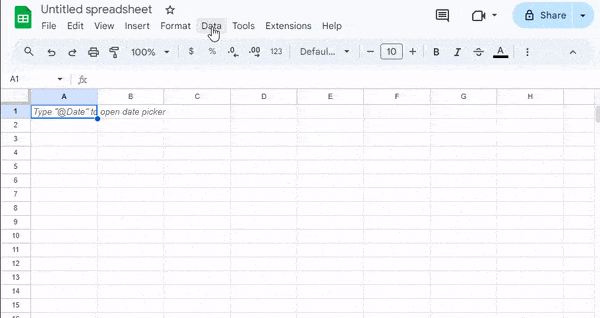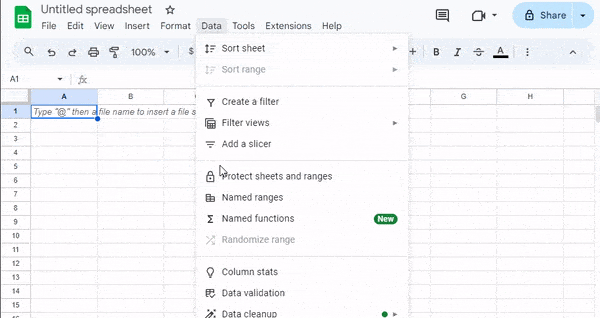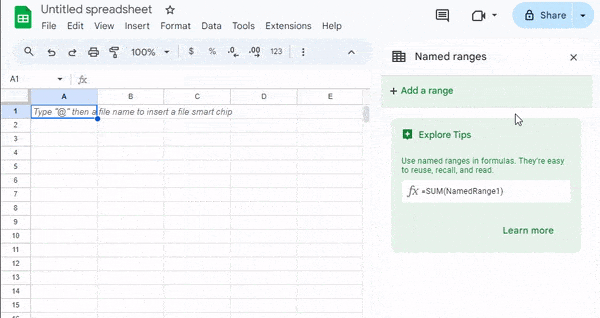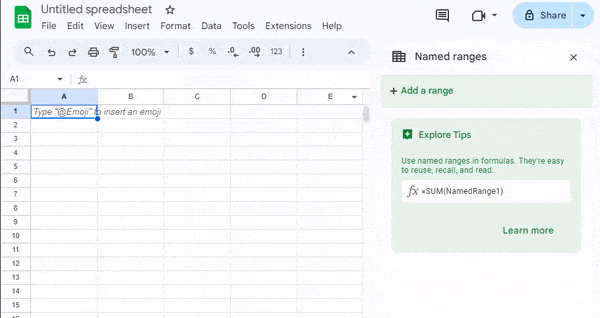
- Function Dragging is a quick way to copy a formula into nearby cells. Click the small blue square in the bottom-right corner of a cell (the fill handle) and drag it across or down to fill the formula into multiple cells automatically.
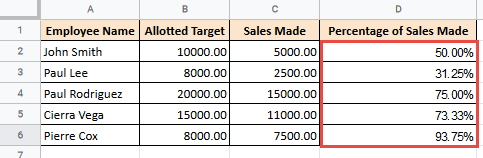
- Nesting Functions combines multiple functions into one powerful formula. For example, you can use
IFinsideSUMto add numbers only if they meet certain conditions. This reduces the number of separate formulas you need and keeps your spreadsheet cleaner.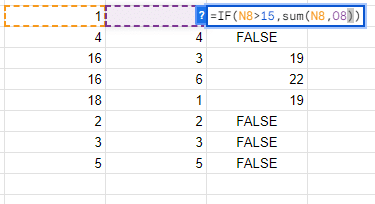
Advanced Google Sheets Features
- Custom Functions
Extend Sheets with your own functions using Google Apps Script. Learn how to write and use them like built-ins via the official guide: Custom Functions in Google Sheets - Pivot Tables
Create dynamic summaries, explore relationships, and aggregate large datasets effortlessly. Get started with step-by-step instructions here: Create & use pivot tables - Data Validation
Ensure clean, accurate data by adding validation rules and dropdowns. Find out how to apply them in Sheets: Google Sheets Help Center
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the best Google Sheets cheat sheet for beginners?
This guide offers a complete set of essential formulas with real world examples, shortcuts, and troubleshooting tips.
2. How do I fix formula errors?
Use IFERROR, TRIM, and autocomplete suggestions to avoid syntax issues and quickly find mistakes.
3. Which formulas should I learn first?
Start with SUM, IF, VLOOKUP, COUNT, and QUERY for a strong foundation.
Why Use a Google Sheets Cheat Sheet
- Quickly reference syntax without searching documentation.
- Improve efficiency by mastering common and advanced functions.
- Discover hidden features to become a power user.
As a reminder, you can print the Google Sheet Formulas Cheat Sheet in pdf format. If you prefer to have this sheet in Word format, you can use Convert PDF to Word to keep the formatting of the Google Sheet cheat sheet in an editable format if you want to include your own notes on the formulas.
Conclusion
This Google Sheets Formulas Cheat Sheet is designed to answer common user questions while providing in depth examples and time saving techniques. Now you can start to practice these functions, and integrate them into your daily workflow. Whether you are analyzing budgets, managing projects, or teaching classes, these tips will help you work smarter and faster in Google Sheets.